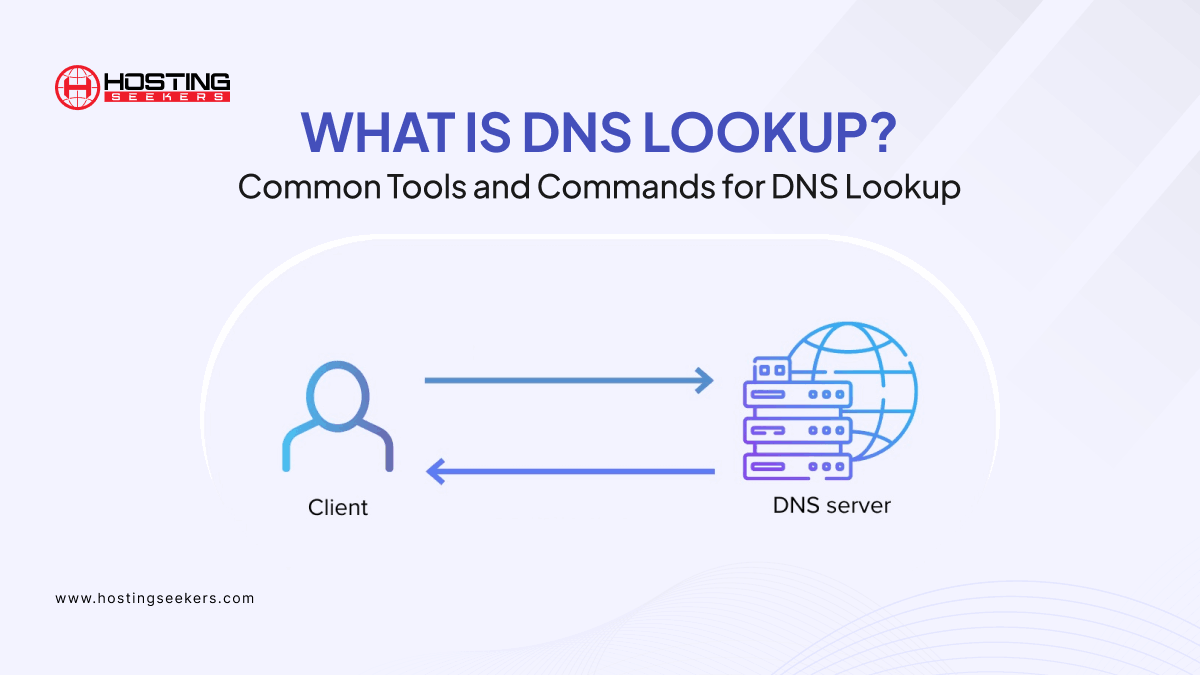
In today's interconnected world, we constantly interact with websites and online services through their domain names (e.g., [invalid URL removed], amazon.com). However, computers don't understand these human-readable names. They rely on IP addresses, unique numerical identifiers assigned to each device on the internet. This is where the Domain Name System (DNS) comes into play.
DNS acts as a crucial translator, mapping human-readable domain names to their corresponding IP addresses. When you type a domain name into your browser, your computer initiates a DNS lookup to find the associated IP address.